All Séance commands are run through the ‘seance’ script that you should already have installed (see installation guide).
Contents
Getting help
Downloading example dataset
Data preprocessing
Preprocessing summary
OTU clustering (454 data)
OTU clustering (non 454 data)
Cluster labelling
Phylogenetic placement of cluster centroids
Inspection with Wasabi
Heatmap visualisations
Getting help
To see details about all seance subcommands and their options type:
seance --help
This also works for individual commands, for example we can see all the options to the ‘preprocess’ command by typing:
seance preprocess --help
Downloading example dataset
For this example we are going to analyse four soil samples from a survey of nematode diversity in temperate rainforests using the 18S rRNA marker gene (see Porazinska et al. 2010 and accession SRX160525 from the short read archive). First we download the .sra archive. dump everything into a FASTQ file and demultiplex the samples. Demultiplexing is performed with a custom script written using BioPython.
wget ftp://ftp-trace.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/sra-instant/reads/ByRun/sra/SRR/SRR522/SRR522901/SRR522901.sra fastq-dump SRR522901.sra wget http://wasabiapp.org/download/seance/tutorial_files/porazinska_demultiplex.py python porazinska_demultiplex.py
FASTQ files are placed in a directory called ‘soil_data’, one sample per file:
grep -c "^+$" soil_data/*fastq soil_data/SRR522901_soil1.fastq:6286 soil_data/SRR522901_soil2.fastq:4697 soil_data/SRR522901_soil3.fastq:16319 soil_data/SRR522901_soil4.fastq:16170
(Alternatively, just download the data from here).
Data preprocessing
Séance requires that there be one sample per file. Unfortunately we do not have the original SFF files so we cannot use the flowgrams to perform denoising, but we can be quite stringent with quality control instead:
seance preprocess --outdir soil_out --forwardprimer TACAAAGGGCAGGGACGTAAT --clipprimers --primererrors 2 --midlength 15 --miderrors 1 --length 250 --qualmethod window --quality 35 --windowlength 50 --chimeras soil_data/*.fastq
This command will preprocess all FASTQ files found in the ‘data’ directory. Séance keeps all of it’s temporary files in a directory specified by the user with the –outdir flag. In this case the directory is called ‘soil_out’. This directory must be stated in all subsequent commands.
The rest of the command states what the forward primer is (–forwardprimer), that the primer sequence is to be removed (–clipprimers) and that we will allow two errors in the primer sequence or else discard the read (–primererrors). The length of the MID (–midlength) is set to 15, the MIDs used in this dataset are actually 11 basepairs, but the four base library key sequence (TCAG) has not been clipped. The MID can contain one error (–miderrors), sequences are truncated to 250 basepairs or else filtered out (–length). Quality filtering is performed in windowed mode (–qualmethod), where the window is 50 basepairs (–window) and must have an average quality of 35 (–quality). Chimeras checking is performed with UCHIME (–chimeras).
Preprocessing summary
We can use the summary command to see statistics about our preprocessing:
seance summary --outdir soil_out
Which in this case outputs:
Filename Length(250) MID(1) Windowed(50)AvgQuality(35) Primer(2) Chimera Homopolymer(8) Ambiguous(N) Accepted Unique
SRR522901_soil1 787 173 2696 9 261 0 41 2319 814
SRR522901_soil2 5 103 2220 5 55 0 28 2281 700
SRR522901_soil3 38 6915 4567 25 69 1 88 4616 1371
SRR522901_soil4 3 5223 5849 17 155 0 100 4823 1491
Totals 833 12414 15332 56 540 1 257 14039 4376
Most of the sequences that were filtered out were due to not meeting the quality threshold (all 50 basepair windows must have an average quality of 35 or greater) or having two many errors in the barcode (MID).
OTU clustering (454 data)
With our data preprocessed we can move on to clustering the sequences into OTUs. By default Séance uses Pagan’s modelling of homopolymer length uncertainty on sequences from platforms known to produce such errors (e.g. Roche/454). This modelling reduces alignment errors around low-complexity regions separated by short spacers and affects the calculation of sequence similarity.
Séance provides several options to control clustering. In this example we state the similarity threshold that defines whether a sequence should be clustered with a centroid sequence (–threshold) and the minimum copy number for a sequence to be included in clustering (–duplicates), ‘–duplicates 2’ effectively removes all singleton sequences.
seance cluster --outdir soil_out --similarity 0.99 --duplicates 2
The cluster subcommand generates two files: soil_out/seance.cluster.fasta and soil_out/seance.cluster.biom, containing the cluster centroid sequences and abundance data, respectively. In this example the four soil samples were found to contain 223 OTUs in total.
Whilst all the count data is stored in the BIOM file format, the count data can also be accessed using the showcounts commands. By default the output is tab separated, but the user can specify the delimiter character (–delimiter) to generate a comma separated value file, for example.
seance showcounts --outdir soil_out > tab_separated.txt seance showcounts --outdir soil_out --delimiter ',' > comma_separated.txt
OTU clustering (non 454 data)
For non 454 data (i.e. for which we do not expect homopolymer errors), use the –nohomopolymer flag:
seance cluster --outdir soil_out --similarity 0.99 --duplicates 2 --nohomopolymer
Cluster labelling
Séance implements a simple method for getting cluster labels by finding the lowest common ancestor in the NCBI taxonomy of all top scoring BLAST hits. Using this approach we find that 77 out of 223 OTUs BLAST to species in the phylum Nematoda:
seance label --outdir soil_out --labels taxonomy --cutoff 0.95
Sometimes labeling can fail due to the NCBI servers being overloaded and requests timeout or otherwise fail. Instead of rerunning the entire label command we can just tell it to get the missing labels:
seance label --outdir soil_out --labels taxonomy --cutoff 0.95 --missing
Or a custom database used (here I have used the SILVA database):
seance label --outdir soil_out --labels blastlocal --cutoff 0.95 --dbfile silva_115_db.fasta
Labels can be inspected with the showlabels command:
seance showlabels --outdir soil_out
Phylogenetic placement of cluster centroids
Séance supports reference-based phylogenetic analysis using Pagan’s phylogenetic placement capabilities ensuring an accurate phylogenetic tree is created even with short amplicon sequences. To perform phylogenetic placement you require a premade multiple sequence alignment (–refalignment) and phylogenetic tree (–reftree), both generated using the complete marker gene. In our case we based the reference on the SILVA alignments (release 115) and inferred a tree using RaXML.
Download the example reference tree and alignment:
curl -O http://wasabiapp.org/download/seance/18S_nematode_reference/SSU_reference_l5_Silva.fasta curl -O http://wasabiapp.org/download/seance/18S_nematode_reference/SSU_reference_l5_Silva.tree
Run the phylogenetic placement:
seance phylogeny --outdir soil_out --refalignment SSU_reference_l5_Silva.fasta --reftree SSU_reference_l5_Silva.tree --subset nematoda
In this example we are only interested in nematodes, so we use the information from the labels to only place the sequences that BLASTed to nematode species (–subset nematoda).
Inspection with Wasabi
Séance has integrated support for viewing phylogeny and multiple sequence alignments with Wasabi (replace XXX with your username):
seance wasabi --outdir soil_out --user XXX
You can see the result by looking at this shared link from Wasabi: http://wasabi2.biocenter.helsinki.fi:8000?share=v04M8s
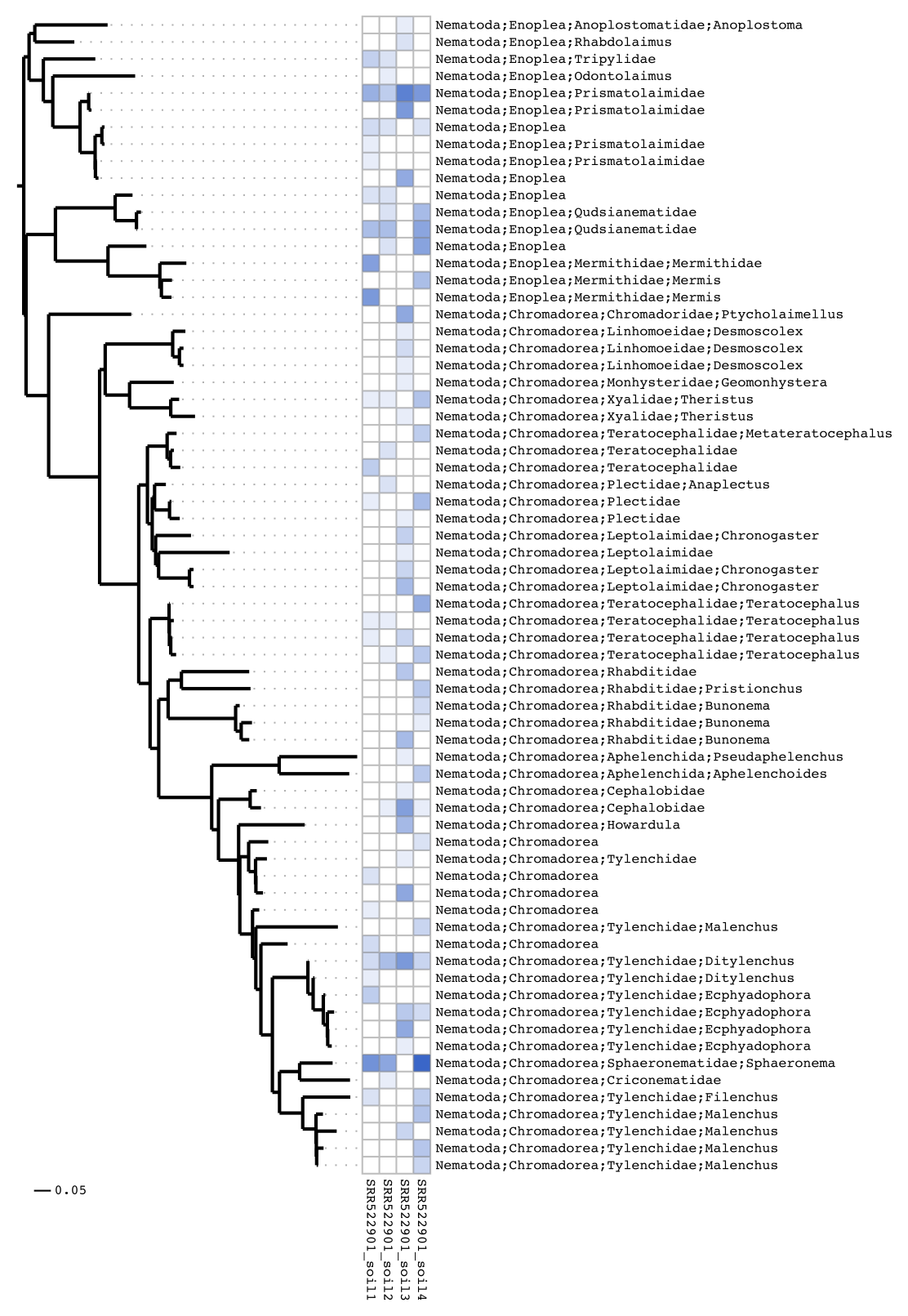
Heatmap visualisations
For publication Séance can create heatmaps integrating the phylogenetic tree:
seance heatmap --outdir soil_out
and without the integrated tree:
seance heatmap --outdir soil_out --notree
There are many options for generating heatmaps, in this final example we do not print the part of the label before ‘Nematoda’ and ladderise the tree:
seance heatmap --outdir soil_out --labelclip nematoda --ladderise